ज्यामिति - Geometry
Hello friends! Today we are going to share a post on GEOMETRY which is an important Chapter for class 9,10,11,12
In Geometry there is many concept and some are more clear but some concepts is clear and give a doubt. We here try to clear you doubts. I request you to I you have an Question then comment we try to solve it and clear your all doubts. You join us on Facebook by All exam Gk And Daily Updated Questions.
Polygon - A polygon is a closed shaped figure with three or more sides
Here are some properties of Polygon
(i) Sum of all the exterior angle of a polygon= 360°
(ii) Each exterior angle of a regular polygon = 360°
(iii) Sum of all the interior angles of a polygon = (n – 2) × 180°
(iv) Each interior angle of a regular polygon =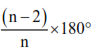
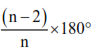
(v) No. of diagonals of a polygon =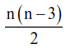
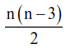
(vi) The ratio of sides a polygon to the diagonals of a polygon is 2 : (n – 3)
(vii) Ratio of interior angle to exterior angle of a regular polygon is (n – 2) : 2
Triangle -A triangle is also a polygon consist of three sides
Properties of triangle:
(i) When one side is extended in any direction, an angle is formed with another side. This is called the exterior angle. There are six exterior angles of a triangle.
(ii) Interior angle + corresponding exterior angle = 180°.
(iii) An exterior angle = Sum of the other two interior opposite angles.
(iv) Sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the length of third side.
(v) Difference of any two sides is less than the third side.
Side opposite to the greatest angle is greatest and vice versa.
(vi) A triangle must have at least two acute angles.
(vii) Triangles on equal bases and between the same parallels have equal areas.
(viii) If a, b, c denote the sides of a triangle then
(i) if c2 < a2 + b2, Triangle is acute angled.
(ii) if c2 = a2 + b2, Triangle is right angled.
(iii) if c2 > a2 + b2, Triangle is obtuse angled.
(ix) If 2 triangles are equiangular, their corresponding sides are proportional. In triangles ABC and∠A=∠X,∠B=∠Y,∠C=∠Z then
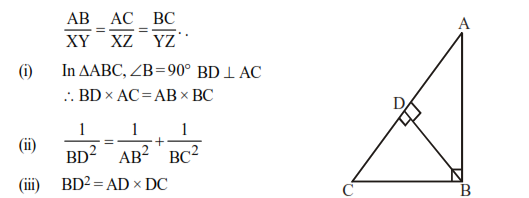
(x) The perpendiculars drawn from vertices to opposite sides (called altitudes) meet at a point called Orthocentre of the triangle.
(xi) The line drawn from a vertex of a triangle to the opposite side such that it bisects the side is called the Median of the triangle. A median bisects the area of the triangle.
(xii) When a vertex of a triangle is joined to the midpoint of the opposite side, we get a median. The point of intersection of the medians is called the Centroid of the triangle. The centroid divides any median in the ratio 2 : 1.
(xiii) Angle Bisector Theorem–
In the figure if AD is the angle bisector (interior) of ∠BAC. Then,
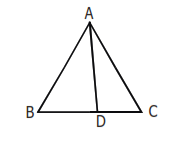
1. AB/AC = BD/DC.
2. AB x AC – BD x DC = AD2
(xiv) Midpoint Theorem –
In a triangle, the line joining the mid points of two sides is parallel to the third side and half of it.
(xv) Basic Proportionality Theorem
A line parallel to any one side of a triangle divides the other two sides proportionally. If DE is parallel to BC, then
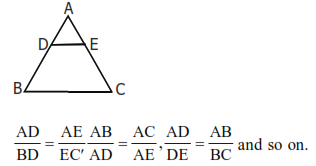
Circle - A circle is a closed shape with a curved boundary. The boundary is formed by a set of that are an equal distance from its center point
Properties of circle –
(i) Only one circle can pass through three given points.
(ii) There is one and only one tangent to the circle passing through any point on the circle.
(iii) From any exterior point of the circle, two tangents can be drawn on to the circle.
(iv)The lengths of two tangents segment from the exterior point to the circle, are equal.
(v) The tangent at any point of a circle and the radius through the point are perpendicular to each other.
(vi) When two circles touch each other, their centres & the point of contact are collinear.
(vii) If two circles touch externally, distance between centres = sum of radii.
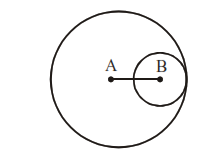
(viii) If two circles touch internally, distance between centres = difference of radii
(ix) Circles with same centre and different radii are concentric circles.
(x) Points lying on the same circle are called concyclic points.
(xi) Measure of an arc means measure of central angle. m(minor arc) + m(major arc) = 360°.
(xii) Angle in a semicircle is a right angle.
(xiii) Only one circle can pass through three given
(xxv) If ON is ^ from the centre O of a circle to a chord AB, then AN = NB.
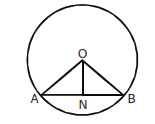
(⊥ from centre bisects chord)
(xv) If N is the midpoint of a chord AB of a circle with centre O, then ∠ONA = 90°.
(Converse,⊥from centre bisects chord)
(xvi) Two congruent figures have equal areas but the converse need not be true.
(xvii) A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two triangles of equal area.
(xviii) Parallelograms on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area.
(xix) Triangles on the same bases and between the same parallels are equal in area.
(xx) If a triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between the same parallels, then the area of the triangle is equal to the half of the parallelogram.
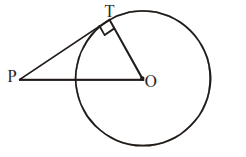
If PT is a tangent to the circle, then OP2 = PT2 = OT2
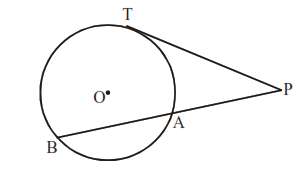
If PT is tangent and PAB is secant of a circle, then PT2 = PA.PB
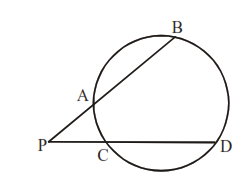
If PB & PD are two secant of a circle, then PA.PB = PC.PD
If two circles touch externally, then distance between their centres = (r1 + r2)
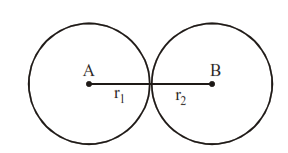
If two circles touch internally, then distance between their centres = r1 – r2 where r1 > r2.
Thanks for coming here
Always give your feedback
Please Share it because "Knowledge increases by sharing"
Comments
Post a Comment